Did you know a single internal link can change how Google ranks your content? Internal linking SEO is one of the most powerful yet underutilized strategies for improving search rankings, distributing authority, and enhancing user experience. If your website isn’t leveraging internal links effectively, you’re missing out on significant traffic and engagement opportunities.
This guide will cover everything from internal linking best practices to advanced strategies like siloing, crawl budget optimization, and link juice distribution. Whether you run an e-commerce site, blog, or SaaS platform, mastering internal linking can transform your SEO results.
What Is Internal Linking SEO?
Internal linking refers to links that point from one page on your website to another page on your website. These links help users and search engines navigate your site, establish content relationships, and pass ranking power between pages.
Unlike external links, which direct users to other domains, internal links pass link equity within your site. This improves crawlability, indexing, and authority distribution—all critical for SEO success.
How Internal Linking Has Evolved with Google’s Algorithm Updates
Google’s approach to internal linking has evolved with updates like Hummingbird, RankBrain, and more recent AI-driven systems. To keep your SEO strategy effective, it’s crucial to stay updated with Google’s latest algorithm changes. We recommend regularly checking Google’s official resources, like the Google Search Central Blog, for the most current insights on how algorithms impact internal linking strategies. This ensures your approach remains aligned with Google’s ever-changing standards.
Internal Linking for SEO vs. User Experience
SEO Benefits of Internal Links
- Boosts PageRank Distribution – High-authority pages can pass link equity to weaker pages.
- Helps Google Discover and Index Pages – Internal links allow search bots to crawl and understand your site faster.
- Improves Keyword Relevance – Anchor text helps Google determine a page’s topic.
- Reduces Orphan Pages – Pages without links are often ignored by search engines.
Related: How internal linking helps new websites rank faster
User Experience Benefits of Internal Links
- Keeps Users Engaged – Adding internal links to related content increases time on site.
- Enhances Navigation – Visitors can find relevant pages more easily.
- Guides Conversions – Internal links can lead users toward important links like product pages, forms, or contact pages.
Example: Good vs. Bad Internal Linking for UX
The image to the right highlights the difference between poor and effective anchor text.
🚫 Bad: “Click Here” – This provides no context for users or search engines about the linked content.
✅ Good: “Check out our guide on internal linking best practices” – This descriptive anchor text improves SEO and user experience by clearly indicating what the link is about.
How Internal Linking Distributes Link Equity (PageRank Simplified)
PageRank assigns value to a page based on the number and quality of links pointing to it. When internal links pass link equity, they strengthen weaker pages.
Related: Using internal links to build topic clusters for better SEO
Example of Link Equity Distribution 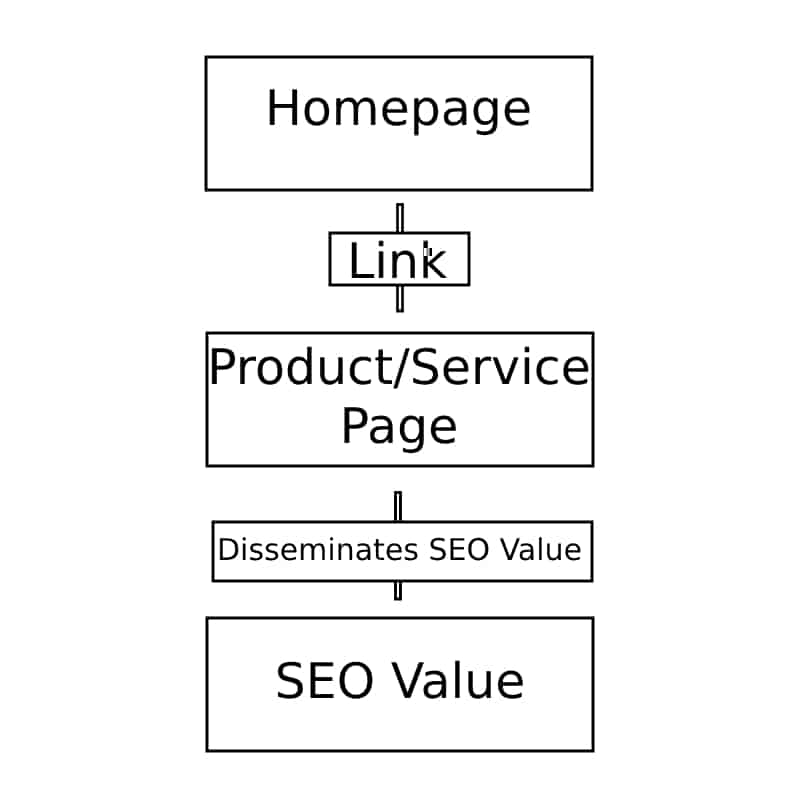
Imagine your homepage has a PageRank score of 90. If you add internal links to three subpages, each may receive 30% of that value. If those subpages then link to product pages, authority continues to flow down.
✅ Best Practice: Ensure your most valuable pages receive strategic internal links from your highest-authority pages.
Types of Internal Links (With Pros and Cons)
1. Navigational Links
- Example: Menu, sidebar, footer links.
- ✅ Helps users find core pages.
- ❌ Does not add much contextual relevance for SEO.
2. Contextual Links
- Example: A blog post linking to a related article.
- ✅ Internal links help Google understand topic relationships.
- ❌ Requires careful keyword-rich anchor text.
3. Footer Links
- Example: Privacy policy, contact, sitemap links.
- ✅ Useful for accessibility and UX.
- ❌ Passes minimal SEO value compared to contextual links.
4. Breadcrumb Links
- Example: Home → Category → Subcategory → Product Page.
- ✅ Improves navigation and SEO hierarchy.
- ❌ Not always necessary for small websites.
5. Image Links
- Example: Clicking a logo directs to the homepage.
- ✅ Can improve engagement when optimized.
- ❌ Needs alt text for Google to understand.
Internal Linking Best Practices
1. Use Descriptive, Keyword-Rich Anchor Text
- ✅ Best: “Learn how to optimize internal links for SEO”
- ❌ Bad: “Click here for more.”
2. Prioritize High-Value Pages
Link to money pages (product pages, service pages) from high-traffic articles.
3. Avoid Orphan Pages
Every new page should have at least one internal link pointing to it.
4. Limit the Number of Links on a Page
Too many links dilute link value passed. Google recommends keeping it reasonable.
5. Regularly Audit and Fix Broken Links
Use Google Search Console or Screaming Frog to identify and repair broken internal links.
Related: Learn more about technical SEO best practices
Internal Linking for E-Commerce Sites
E-commerce websites require a structured internal linking strategy to ensure product pages rank.
E-Commerce Best Practices:
- Link Product Pages to Category Pages – Helps distribute authority.
- Use Breadcrumb Navigation – Enhances UX and SEO.
- Interlink Blog Content to Products – Drives conversions.
✅ Example: A shoe store blog post on “Best Running Shoes” should add links to relevant product pages.
Related: How schema markup enhances internal linking for SEO
SEO Tools for Internal Linking Analysis
1. Free Tools
- Google Search Console – Finds pages with low internal link counts.
- Screaming Frog (Free Version) – Crawls up to 500 URLs.
2. Paid Tools
- Ahrefs – Tracks internal link equity and anchor text usage.
- SEMrush – Offers a detailed internal linking suggestion tool.
- Moz Pro – Provides an Internal Links report to analyze how pages link to each other, detect weakly linked content, and improve overall site architecture.
Step-by-Step: Finding Orphan Pages in Google Search Console

- Log into Google Search Console and select your website.
- Go to Pages (under “Indexing” in the left-hand menu).
- Scroll down to the “Why pages aren’t indexed” section.
- Look for statuses like:
- “Discovered – currently not indexed”
- “Crawled – currently not indexed”
- “Not found (404)” (if the page was previously linked but now missing)
- Click on a specific page URL to analyze it. If it’s important, ensure it has internal links pointing to it from relevant pages.
This method helps identify pages that Google knows about but hasn’t indexed—often because they lack strong internal links. Fixing these issues can improve crawlability and search rankings.
Related: Using Google Search Console to audit internal links and find orphan pages
How to Measure the Impact of Internal Linking SEO
Key Metrics to Track:
- Organic Traffic – Use Google Analytics to measure traffic changes.
- Bounce Rate – Lower bounce rates indicate better internal linking structure.
- Pages Per Session – More links within content should increase engagement.
✅ Example: A study by Ahrefs found that pages with more internal links rank higher for competitive keywords.
Final Thoughts: Strengthen Your Internal Linking Strategy
A well-structured internal linking strategy can boost rankings, enhance user experience, and drive conversions. Whether you’re fixing broken links, improving internal linking for SEO, or optimizing for mobile, every improvement helps.
Struggling to optimize your internal links? LuccaAM can audit your site, fix internal linking issues, and improve your rankings. Contact us today for a free consultation!
Related: Future-proofing your SEO strategy with smart internal linking
FAQs
What is the difference between internal and external linking for SEO?
Internal links connect pages within your site, while external links point to other domains. Both help SEO but serve different purposes.
How can internal linking improve my site’s crawl budget?
Internal links ensure search engines discover and prioritize important pages, optimizing crawl efficiency.
Should I use internal links in my blog posts?
Yes! Adding internal links keeps users engaged, improves SEO, and distributes authority across your site.
How do I find and fix orphan pages on my website?
Use Google Search Console to identify pages with no internal links pointing to them and add strategic internal links.
- Content Pruning: The Key to Better SEO and Higher Rankings - March 25, 2025
- Internal Linking SEO: How to Boost Your Rankings and User Experience - February 18, 2025
- Featured Snippet Optimization: How to Dominate the Top of Google Search Results - January 17, 2025

